INTRODUCTION
The endothelial cell growth supplement (ECGS) is a bovine neural tissue extract containing growth-promoting factors for mammalian vascular endothelial cells and can improve the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). ECGS is crucial for the differentiation and proliferation of endothelial cells. It can coordinate with interleukin-1 (IL-1) and mediate matrix remodeling in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC).
ECGS is prepared by modifying the method of Maciag et al. and is lyophilized from a sterile solution containing NaCl and streptomycin sulfate. It has been reported that ECGS, as a medium supplement, can play a positive role in the fusion and growth of hybridoma cells for monoclonal antibody production.
PRODUCT NOTICES
1.After receiving the product, reconstitute it and then aliquot into small volumes for storage at -20℃ for up to 6 months or at 2~8℃ for no more than one week. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
2.This product is intended for use by professionals for scientific research only and is not to be used for clinical diagnosis or treatment, food, or pharmaceuticals. It should not be stored in a residential area.
3.For your safety and health, please wear a lab coat and disposable gloves during operation.
STORAGE AND STABILITY
Store at -20°C in the dark for 12 months.
Shipping Conditions
Wet ice transportation.
Product Data Display
- Cell Morphology
Method: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured for 72 hours using PWL224 and S brand ECGS. The cell morphology was observed under a microscope.
Results: As shown in the images below, HUVECs cultured with PWL224 and the imported S brand ECGS exhibited consistent morphology, displaying typical epithelial-like characteristics.
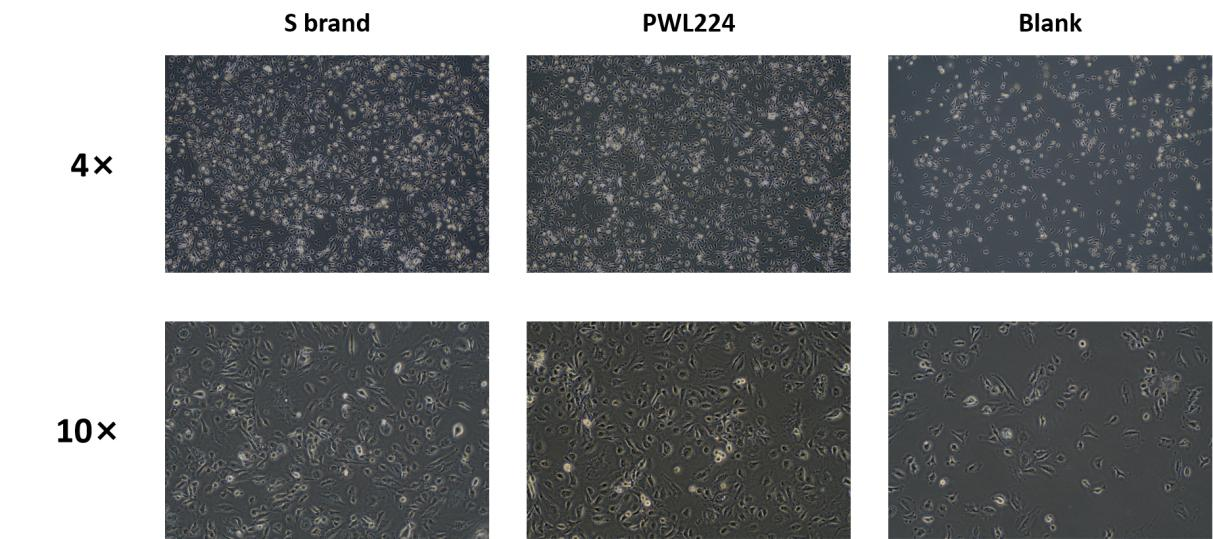
Figure 1. Morphology of HUVECs
- Cell Proliferation
Method: HUVEC cells were seeded into a 6-well plate at a density of 2×10^5 cells per well, divided into three groups: PWL224, S brand, and a blank control. They were cultured under identical conditions for 72 hours, after which the number of cells and viability per well were assessed.
Results: As shown in the table below, the number of cells in both the PWL224 group and the imported S brand group was more than 1.5 times that of the blank control group, and the viability was also significantly higher than the blank control. Additionally, at the same ECGS concentration, the cell proliferation and viability in the PWL224 group were higher than in the imported S brand group.
Table 1. Effect of ECGS on HUVEC Cell Proliferation and Viability
| ECGS | 0 hours | 72 hours | |||
| Vendor | Concentration (μg/mL) | Cell Count (×10^5) | viability | Cell Count (×10^5) | viability |
| Blank Control | 0 | 2 | 85.20% | 3.18 | 79.77% |
| PWL224 | 30 | 2 | 85.20% | 5.56 | 85.30% |
| 60 | 2 | 85.20% | 6.15 | 90.03% | |
| S brand | 30 | 2 | 85.20% | 5.43 | 83.60% |
| 60 | 2 | 85.20% | 5.52 | 87.47% | |
- Protein Distribution
Method: Both PWL224 and S brand ECGS were subjected to protein electrophoresis using a 4-20% HEPES gel. The sample amount was 5 μg, and the electrophoresis was conducted for 50 minutes.
Results: As shown in Figure 2, the protein bands for PWL224 appear darker compared to the imported S brand, indicating a higher protein concentration. However, the distribution of protein bands is consistent between PWL224 and the imported S brand.
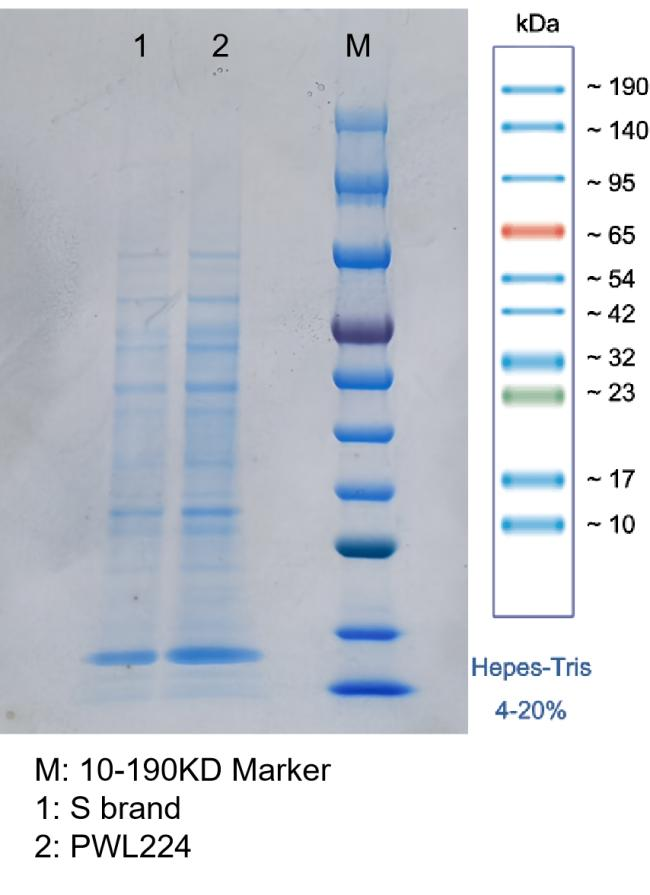
Figure 2. ECGS Protein Electrophoresis